Answers
Fnet=ma
Fnet=300•2
Fnet=600N
Related Questions
A circuit component that is a composed of a semiconductor layer sandwiched between two other semiconductor layers is a(n)?
Answers
Explanation:
It's a transistor. Hope that helps!
Answer:
D. Transistor
Explanation:
Edge 2021
Thermal effects refers to the:
Answers
Answer:
removal of heat by cooling towers
calculate the force between charges 4x10^-8c and 1.8x10^-6C if they wre 3.5 m apart?
Answers
Answer:
no se pregúntale a otro gracias cuidate :)
2. A kayaker is paddling south at 2.50 m/s, and encounters a weird current moving 1.15 m/s west.
What is the resultant velocity?
Answers
Answer:
v = 2.91 m/s
Explanation:
Given that,
A kayaker is paddling south at 2.50 m/s, and encounters a weird current moving 1.15 m/s west.
We need to find the resultant velocity. Both velocities are perpendicular to each other. So,
\(v=\sqrt{v_1^2+v_2^2} \\\\=\sqrt{2.5^2+1.5^2} \\\\=2.91\ m/s\)
So, the magnitude of the resultant velocity is equal to 2.91 m/s.
Water flows at a speed of 13 m/s through a pipe that has a diameter of 1.2 m. What is the
diameter of the smaller end of the pipe that the water comes out with a speed of 30 m/s?
Answers
The diameter of the smaller end of the pipe is approximately 0.78 meters.
To determine the diameter of the smaller end of the pipe, we can use the principle of conservation of mass. According to this principle, the mass flow rate of water should remain constant throughout the pipe.
The mass flow rate is given by the equation:
Mass flow rate = density of water * cross-sectional area * velocity
Since the density of the water remains constant, we can write:
Cross-sectional area1 * velocity1 = Cross-sectional area2 * velocity2
Given that the velocity1 is 13 m/s, the diameter1 is 1.2 m, and the velocity2 is 30 m/s, we can solve for the diameter2 using the equation:
(pi * (diameter1/2)^2) * velocity1 = (pi * (diameter2/2)^2) * velocity2
Simplifying the equation:
(1.2/2)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Calculating the equation:
(0.6)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
0.36 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
4.68 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Dividing both sides by 30:
0.156 = (diameter2/2)^2
Taking the square root of both sides:
0.39 = diameter2/2
Multiplying both sides by 2:
0.78 = diameter2
To learn more about diameter
https://brainly.com/question/32968193
#SPJ8
Which current is produced in homes
Answers
Hope this helped xxxx
Answer:
answer is C on edge 2021
Explanation:
A fishing line will break when the tension in it reaches 15 N. A 3.1 m length of it is used to tie a model aeroplane of mass 280 g to a post so it goes round in circles. What is the fastest speed the aeroplane can reach before the line breaks. Give your answer both as an angular velocity and in m/s.
Answers
Answer:
F = m v^2 / R maximum centripetal force
v^2 = 15 * 3.1 / .28 = 166 m^2/s^2
v = 12.9 m/s maximum speed
v = ω R speed as related to angular speed
ω = 12.9 m/s / 3.1 m = 4.2 / sec max angular speed
The angular velocity of the airplane is 4.157 rad/s and the linear velocity is 12.887 m/s.
What is the angular velocity?The angular velocity of an object can be described as the velocity to move within a speed w.r.t. its center of rotation. Angular velocity can be defined as equal to the angular displacement, which is theta.
The mathematical expression to determine angular velocity is:
ω =Δθ/Δt
where Δθ represents the change in angular rotation, ω represents the angular velocity, and Δt represents the change in time.
Given , F = 15 N, m = 280 g, and r = 3.1 m
The centripetal force, F = mω²r
15 = 0.28 × ω² × 3.1
ω = 4.157 rad/s
To determine linear velocity, we need the formula, v = ωr
v = 4.157 × 3.1
v = 12.887 m/s
Therefore, the angular velocity is equal to 12.887 m/s.
Learn more about angular velocity, here
brainly.com/question/1980605
#SPJ2
The sound from a clarinet at a distance of 5 m from a sound level meter is found to be 52 dB. If
the frequency is 1000 Hz, find (a) the sound loudness level in phons, (b) the sound intensity in
watts/meter2, and (c) the power of the source in watts.
Answers
There are 90 phones of volume, 10-7 W/m2 of sound intensity, and 0.0314 watts of source power.
Which frequency is the simplest?A straightforward frequency analysis compares the values of the fields you provide and generates a report listing each value for those fields along with the frequency at which each value occurs.
How often does sound occur?The rate at which a sound power wave repeats itself, also known as frequency or pitch, is measured in cycles per second. Bullfrog calls and cricket chirps have lower frequencies than drum beats and whistles, respectively.
To know more about Frequency visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14316711
#SPJ1
How will you describe the graphs of a. distance vs. time b. distance vs. time²
Answers
Answer:
a/b^2=velocity
Explanation:
What does volume measure name two different units that might be used to measure volume
Answers
Answer:
Volume measures liquid
Explanation:
Volume can be measured in meters and centimeters
What kind of energy do plants convert light energy from the sun
Answers
Answer: chemical energy
Explanation:
7. Four perpendicular forces, 2 N, 3 N, 9 N and 10 N act on object P as shown in Diagram 2. 10 N A B 9 N 3 N 2 N P Diagram 2 What is the magnitude of the resultant force? 10 N C 18 N 14 N D 20 N

Answers
Answer: R=
A
2
+B
2
+2ABcosθ
θ=90
o
cos90
o
=0
R=
A
2
+B
2
=
3N
2
+4N
2
=5N
Explanation:
A soccer ball, kicked from ground level at an angle of 64.0° above horizontal, is in the air for 3.40 s. What was its initial speed, in m/s, just after it was kicked? Ignore air resistance.
Answers
A soccer ball, kicked from ground level at an angle of 64.0° above horizontal, is in the air for 3.40 s. The initial speed, in m/s, just after it was kicked will be 76.07 m/s
The branch of physics that defines motion with respect to space and time, ignoring the cause of that motion, is known as kinematics. Kinematics equations are a set of equations that can derive an unknown aspect of a body’s motion if the other aspects are provided.
given
v = 0
g = 9.8 m/\(s^{2}\)
t = 3.40 s
u = ?
cos(theta) = 64°
v = u*cos(theta) - g*t
0 = u * cos(64) - 9.8*(3.40)
u = 76.07 m/s
The initial speed, in m/s, just after it was kicked will be 76.07 m/s
To learn more about Kinematics equations here
https://brainly.com/question/28712225
#SPJ1
the answer for this pls

Answers
The solubility of a substance in a solvent is affected by many factors, including temperature. In general, increasing the temperature of a solvent increases the solubility of a solute in that solvent. This relationship is known as the temperature-solubility relationship.
How to explain the relationshipThere are a few different ways in which temperature can affect solubility, depending on the specific solute and solvent in question. For example:
For most solid solutes in liquid solvents, increasing the temperature of the solvent will increase the solubility of the solute. This is because increasing the temperature generally increases the kinetic energy of the solvent molecules, which in turn makes it easier for them to break apart the intermolecular forces holding the solute together and form new solute-solvent interactions.
In some cases, however, the opposite may be true: the solubility of a solute in a solvent may decrease with increasing temperature. This is often observed for gases dissolved in liquids, where increasing the temperature decreases the solubility of the gas. This is because increasing the temperature of the liquid also increases the kinetic energy of the gas molecules, making them more likely to escape from the liquid and form a gas phase.
In rare cases, the temperature-solubility relationship may be more complex and exhibit unusual behavior. For example, for some solutes, the solubility may initially increase with temperature but then decrease at higher temperatures.
Overall, the relationship between temperature and solubility is an important consideration in many chemical processes, including crystallization, precipitation, and dissolution. Understanding this relationship can help scientists and engineers optimize their processes and achieve their desired outcomes.
Learn more about temperature on
https://brainly.com/question/25677592
#SPJ1
For number 6 I really can't figure out the answer does anyone know ?

Answers
The factor that leads to loess deposit is when the wind carries fine sediment. That is option C.
What are loess deposits?The loess deposits are those deposits that are usually found at the edge of deserts.
The major factor that causes the formation of loess is the wind because they are entrained, transported, and deposited by the wind.
The fine particles carried by wind contains find grained sediments, organic particles that are capable of forming loess.
Learn more about wind here:
https://brainly.com/question/29801913
#SPJ1
How many meters is in 20,000 miles
Answers
Answer:
32186880 metres
AreaData Transfer RateDigital StorageEnergyFrequencyFuel EconomyLengthMassPlane AnglePressureSpeedTemperatureTimeVolume
kilometreMeterCentimeterMillimetremicrometresNanometreMileYardFootInchNautical mile
kilometreMeterCentimeterMillimetremicrometresNanometreMileYardFootInchNautical mile
Formula
for an approximate result, multiply the length value by 1609
More info
Feedback
Answer: 32186880 Meters.
I really hope this helps, don't know if you needed an Explanation.
Which is more soluble in 100mg of water at the same temperature?
A. Copper (II) Sulfate
B. Potassium Sulfate
Answers
Answer:
A. Copper (||) sulfate
Explanation:
just got it right on quizlet
The centripetal acceleration of a point on a wheel is 72 m/s2. The wheel is spinning with a
tangential velocity of 4.3 m/s. What is the radius of the wheel?
Answers
The radius of the wheel with a tangential velocity of 4.3 m/s and centripetal acceleration of 72 m/s² is 0.25 meter.
What is centripetal acceleration ?The acceleration of an object ,moving through a circular path is called the centripetal acceleration. It is related to the velocity and radius of curvature of the circular path as follows:
a = v²/r.
The tangential velocity or angular velocity is the rotational analogue of the linear velocity.
given that, tangential velocity v = 4.3 m/s
centripetal acceleration a = 72 m/s²
Then, radius of the wheel is calculated as follows:
r = v²/a
r = (4.3 m/s × 4.3 m/s)72 m/s²
= 0.25 meter.
Therefore, the radius of the rotating wheel is 0.25 meter.
Find more on centripetal acceleration:
https://brainly.com/question/29197591
#SPJ9
An object with a mass of 5.5 kg is allowed to slide from rest down an inclined plane. The plane makes an angle of 30o with the horizontal and is 72 m long. The coefficient of friction between the plane and the object is 0.35. The speed of the object at the bottom of the plane is:_________.
a. 24 m/s.
b. 11 m/s.
c. 15 m/s.
d. 5.3 m/s.
e. 17 m/s.
Answers
Answer:
The speed will be "16.67 m/s".
Explanation:
The given values are:
Distance
= 72 m
Angle
= 30°
Acceleration
= \(g(sin \theta-ucos \theta)\)
= \((9.8\times sin30^{\circ}) - (0.53\times cos30^{\circ})\)
= \(1.929 \ m/s^2\)
Let the speed be "v".
⇒ \(v^2=u^2+2as\)
⇒ \(v^2=0(2\times 1.929\times 72)\)
⇒ \(v^2=277.226\)
⇒ \(v=\sqrt{277.776}\)
⇒ \(v=16.67 \ m/s\)
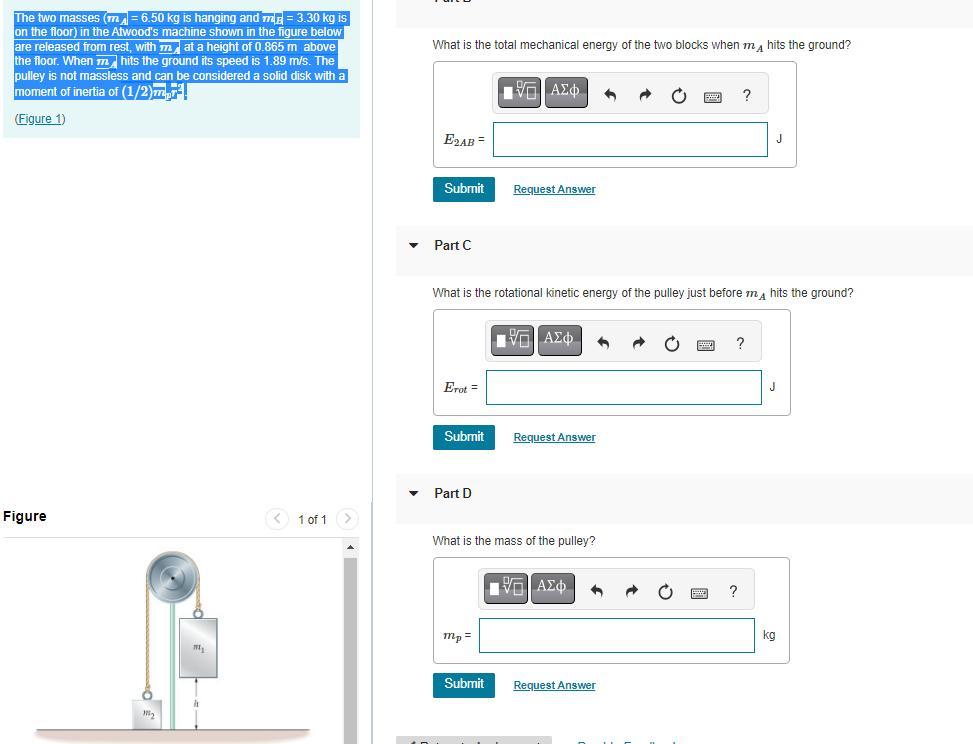
The two masses (mA
= 6.50 kg is hanging and mB
= 3.30 kg is on the floor) in the Atwood's machine shown in the figure below are released from rest, with mA
at a height of 0.865 m above the floor. When mA
hits the ground its speed is 1.89 m/s. The pulley is not massless and can be considered a solid disk with a moment of inertia of (1/2)mpr2
.
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest?
(Figure 1)
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA
hits the ground?
Part C
What is the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA
hits the ground?
Part D
What is the mass of the pulley?
Answers
A)The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
B).The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J
C) The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.
D) The mass of the pulley ismp = (1/2)mpr²/R² =(1/2)(0.020 kg)(0.100 m)²/(0.200 m)² = 0.001 kg = 1 g.r = (1/2)R.
The Atwood's machine shown in Figure 1 consists of two masses mA = 6.50 kg and mB = 3.30 kg. The height of mA above the floor is 0.865 m. When mA hits the floor, its velocity is 1.89 m/s. The pulley has a moment of inertia (1/2)mpr². We have to find the total mechanical energy of the two blocks before they are released, the total mechanical energy when mA hits the ground, the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground, and the mass of the pulley. Let's solve these one by one. Part A The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
The equation for gravitational potential energy is mgh. The gravitational potential energy of mA and mB is mAg(h-hB)where h is the height of mA above the floor and hB is the height of mB above the floor. Since the pulley is at the same height as mB, its gravitational potential energy ismBg(h-hB).The gravitational potential energy of mA is6.50 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 0.865 m = 54.33 J.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J.Part BThe total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground can be found by adding the kinetic energy of mA, the kinetic energy of mB, and the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley to the gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley. The equation for kinetic energy is (1/2)mv². The kinetic energy of mA is(1/2) × 6.50 kg × (1.89 m/s)² = 11.54 J.The kinetic energy of mB is(1/2) × 3.30 kg × 0 m/s² = 0 J, since it is at rest.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω²,where R is the radius of the pulley and ω is its angular velocity just before mA hits the ground. We can use the fact that the linear speed of the rope is the same on both sides of the pulley to find ω. The equation for linear speed is v = Rω. When mA hits the ground, its speed is 1.89 m/s. The speed of mB is zero. Since the rope is inextensible, the speed of the rope is also 1.89 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the pulley is also 1.89 m/s. We can find the angular velocity of the pulley by dividing the linear velocity by the radius.ω = v/R = 1.89 m/s ÷ (0.200 m/2) = 18.9 rad/s.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω² =(1/4)mpR²ω² =(1/4)mp(0.200 m)²(18.9 rad/s)² =(0.178 mp) J.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground is11.54 J + 0 J + 0 J + (0.178 mp) J = 11.72 J + (0.178 mp) J.Part CThe rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.Part DWe can find the mass of the pulley by using the moment of inertia of a disk and the mass of the pulley. The moment of inertia of a disk is (1/2)mr². Therefore,(1/2)mpR² = (1/2)mpr²,where R is the radius of the pulley and r is the radius of gyration of the pulley. The radius of gyration of a disk is (1/2)R.
for such more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
A body is travelling with a velocity 30 m/s².what will be its velocity after 4s?
Answers
Answer:
70m/s²
Explanation:
we will use the first equation of Dalton to find it
A car of mass 500kg travelling at 60m/s has it speed reduced to 40m/s by a constant breaking force over a distance of 200m. find car initial kinetic energy. the final kinetic energy
Answers
Answer:
Ek1 = 900000 [J]
Ek1 = 400000 [J]
Explanation:
In order to solve this problem we must remember that kinetic energy is defined as the product of mass by velocity squared by a medium. Therefore using the following equation we have:
\(E_{k1}=\frac{1}{2}*m*v1^{2}\)
where:
m = mass = 500 [kg]
v1 = 60 [m/s]
So we have:
Ek1 = 0.5*500*(60^2)
Ek1 = 900000 [J]
and:
Ek2 = 0.5*500*(40^2)
Ek2 = 400000 [J]
It is now 9:11 a.m. but when the bell rings at 9:12 a.m. Susie will be late for Mrs. Garner's U.S. History class for the 3rd time this week. She must get from one side of the school to the other by hurrying down three different hallways. She runs down the first hallway (D-Hall), a distance of 47.0 meters. The second hallway (C-Hall) is filled with students, and she covers its 63.0 m length quickly. The final hallway (B- Hall) is empty, and Susie sprints its 76.0 m length. How fast does Susie need to go to make it to class on time (Hint: Calculate the total distance. Then calculate her total average speed rounded to the nearest tenths in meters/seconds.)?
Answers
Answer:
3.1 m/s
Explanation:
The total distance she has to run is the addition of the three lengths:
47 + 63 + 76 = 186 meters.
She needs to cover it one minute (60 seconds). Therefore her speed must be:
186 m / 60 s = 3.1 m/s
100 POINTS AND BRAINLIEST! What were the Magdeburg Hemispheres?
Answers
Answer:
Magdeburg hemispheres are two half-spheres of equal size. Placing them together traps air between them. This air is merely trapped, and not compressed, so the pressure inside is the same as the pressure of the atmosphere outside the spheres. The spheres thus pull apart with nearly no resistance.
The Magdeburg hemispheres are a pair of large copper hemispheres, with mating rims. They were used to demonstrate the power of atmospheric pressure. When the rims were sealed with grease and the air was pumped out, the sphere contained a vacuum and could not be pulled apart by teams of horses.
A coil 4.15 cm radius, containing 560 turns, is placed in a uniform magnetic field that varies with time according to B=( 1.20×10−2 T/s )t+( 3.40×10−5 T/s4 )t4. The coil is connected to a 530-Ω resistor, and its plane is perpendicular to the magnetic field. You can ignore the resistance of the coil.
(a) Find the magnitude of the induced emf in the coil as a function of time.
(b) What is the current in the resistor at time t = 5.00 s?
Answers
Answer:
(a) \(\epsilon=0.036V+4.119*10^{-4}\frac{T}{s^4}m^{-2}t^3\)
(b) I = 1.65*10^-4 A
Explanation:
(a) To find the induced emf in the coil you use the following formula:
\(\epsilon=N|\frac{d\Phi_B}{dt}|\) (1)
N: turns = 560
ФB: magnetic flux = AB
A: area = π r^2 = π (0.0415m)^2 = 5.41*10^-3 m^2
you replace the expression for the magnetic flux in the equation (1). Next, you derivative the magnetic field respect to time. Finally, you replace t=5.00s:
\(\epsilon=(560)|\frac{d(AB)}{dt}|=(560)(5.41*10^{-3}m^2)|\frac{dB}{dt}|\\\\B=( 1.20*10^{-2} T/s )t+( 3.40*10^{-5} T/s^4 )t^4\\\\\frac{dB}{dt}=(1.20*10^{-2}+1.36*10^{-4}T/s^4)t^3\frac{T}{s}\\\\\epsilon=(560)(5.41*10^{-3}m^2)(1.20*10^{-2}+(1.36*10^{-4}T/s^4)t^3)\\\\\epsilon=(3.029m^2)(1.20*10^{-2}\frac{T}{s}+(1.36*10^{-4}T/s^4)t^3)\\\\\epsilon=0.036V+4.119*10^{-4}\frac{T}{s^4}t^3\)
(b) The current is given by:
\(I=\frac{\epsilon}{R}=\frac{0.036V+4.119*10^{-4}T/s^4(5.00s)^3m^{-2}}{530\Omega}\\\\I=1.65*10^{-4}A\)
Can someone please answer this? I am really lost.

Answers
Answer:
8.0 rad/s
Explanation:
I₁ = 1.0 kgm², ω₁ = -20.0 rad/s (clockwise is positive direction)
I₂ = 4.0 kgm², ω₂ = 15.0 rad/s
Angular momentum conservation:
I₁ω₁ + I₂ω₂ = (I₁ + I₂)ω
1.0 x (-20.0) + 4.0 * 15.0 = (1.0 + 4.0)ω
40.0 = 5.0ω
so ω = 8.0 rad/s
Which event is an example of condensation?
O A. Ice forms on the surface of a puddle. O B. Fog disappears when the Sun vomes out. O C. The outside of a glass of ice water becomes moist. O D. Perspiration dries on a person's skin.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
As warm air comes in contact with the glass, the air becomes cooler. When that happens the cool air can't hold as much water vapor which condenses on the glass.
The answer is C.
A car is traveling at 15m/s on a horizontal road. the brakes are applied and the car skids to a stop in 4.0s . the coefficient of Kinetic friction between the tires and road is:_________.
A) .38
B) .69
C) .76
D) .92
E) 1.11
Answers
Answer:
the coefficient of Kinetic friction between the tires and road is 0.38
Option A) .38 is the correct answer
Explanation:
Given that;
final velocity v = 0
initial velocity u = 15m/s
time taken t = 4 s
acceleration a = ?
from the equation of motion
v = u + at
we substitute
0 = 15 + a × 4
acceleration a = -15/4 = - 3.75 m/s²
the negative sign tells us that its a deacceleration so the sign can be ignored.
Deacceleration due to friction a = μ × g
we substitute
3.75 = μ × 9.8
μ = 3.75 / 9.8 = 0.3826 ≈ 0.38
Therefore the coefficient of Kinetic friction between the tires and road is 0.38
Option A) .38 is the correct answer
How is the A He related to the A Hof a reaction?
Answers
Answer:
by giving a person to person
Calculate the quantity of heat energy which must be transferred to 2.25 kg of brass to raise its temperature from 20°C to 240°C if the specific heat of brass is 394 J/kgK.
Answers
The quantity of heat energy that must be transferred to 2.25 kg of brass to raise its temperature from 20 °C to 240 °C is 195030 J
How do i determine the quantity of heat energy?First, we shall list out the given parameters from the question. This is shown below:
Mass of brass (M) = 2.25 Kg Initial temperature of brass (T₁) = 20 °CFinal temperature of brass (T₂) = 240 °CChange in temperature of brass (ΔT) = 240 - 20 = 220 °CSpecific heat capacity of brass (C) = 394 J/kgKQuantity of heat energy (Q) =?The quantity of heat energy that must be transferred can be obtained as follow:
Q = MCΔT
= 2.25 × 394 × 220
= 195030 J
Thus, we can conclude quantity of heat energy that must be transferred is 195030 J
Learn more about heat:
https://brainly.com/question/16398667
#SPJ1