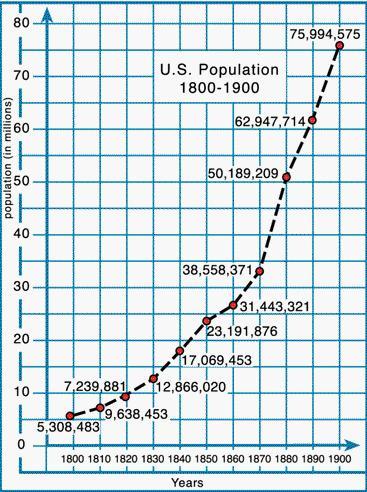
Answers
Answer:
3. years
Explanation:
The independent variable is the x axis of graph
Related Questions
The star Mintaka in the Orion constellation is about 30x larger than our sun with a radius of 5.74 x 10^9 m. It's surface temperature is about 29,500 K. Consider the spherical surface to behave as a blackbody radiator. What is the rate at which energy is radiated from this star, to 3 sig fig?

Answers
Due to the body is a blackbody e=1
\(\begin{gathered} P=5.6703\cdot10^{-8}\cdot(\pi\cdot(5.74\cdot10^9)^2)\cdot(29500^4-2.7^4) \\ P=4.445\cdot10^{30}W \end{gathered}\)This is the rate of energy over time that this star radiates
You put your book on the bus seat next to you. When the bus stops suddenly the book slides forward off the seat. Why?
A.) The book received a push from the seat hitting it.
B.) The force applied by the bus caused it to accelerate forward.
C.) The book's inertia carried it forward.
D.) The book could never slide forward to begin with.
Answers
Answer:
C) The book's inertia carried it forward.
When the bus stops suddenly, the book tends to remain in motion due to its inertia. The book was at rest on the seat of the bus, and when the bus stopped suddenly, the book continued moving forward with the same speed and direction it had before the bus stopped. As a result, the book slid off the seat and onto the floor.
what does an object made before it can be performed work
Answers
Answer:
In order to accomplish work on an object there must be a force exerted on the object and it must move in the direction of the force
Explanation:
A measure of energy expended in moving an object; most commonly, force times displacement. No work is done if the object does not move.
HOPE IT HELPS
BRAINLIEST PLEASE!
A bowling ball and a baseball both roll across your foot at the same speed. The bowling ball hurts much more.
Which law of motion is this?
Answers
Answer:
Newtons second law
Explanation:
Depends on mass
Answer:
2nd law
Explanation:
:))))))))))))))
A 1250 kg car is stopped at a traffic light. A 3550 kg truck moving at 8.33 m/s strikes the car from behind, causing the bumpers to lock together.
A) What is the momentum of the car-truck system before the collision?
B) What is the momentum of the car-truck system after the collision?
C) How fast do the car and truck move after the collision?
(Do NOT put any links or reproductions, I just need help with this.)
Answers
A) Before the collision, the total momentum is
(1250 kg) (0 m/s) + (3550 kg) (8.33 m/s) ≈ 29,600 kg•m/s
B) Momentum is conserved, so after the collision it is still approximately 29,600 kg•m/s.
C) If v is the speed of the locked car-truck system, then
(1250 kg) (0 m/s) + (3550 kg) (8.33 m/s) = (1250 kg + 3550 kg) v
Solve for v :
29,571.5 kg•m/s = (4800 kg) v
v ≈ 6.16 m/s
A wave is traveling through a 40.0-meter-long cable strung with a tension of 35,000 newtons. The mass of this length of cable is 10.2 kilograms. What is the speed of a wave that is traveling in the cable?
Answers
Answer:7678
Explanation:
A bus of mass 2500 kg goes round a corner of radius 50 m at a speed of 5 m/s. What force is needed for the bus to go round the corner?
Answers
Answer:
force needed for the bus to go round the corner is 50,000 N.
Explanation:
To find the force needed for the bus to go round the corner, we can use the formula for centripetal force:
F = (mv^2)/r
where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object, v is the velocity of the object, and r is the radius of the circular path.
Plugging in the values given in the problem, we get:
F = (2500 kg)(5 m/s)^2 / 50 m
= 50,000 N
So the force needed for the bus to go round the corner is 50,000 N.
Use the vocabulary words from
“Read It” to complete the
following sentences.
Light from the Sun reaches Earth very
quickly. The (4)_____ is 186,000 miles per
second! We capture sunlight using
(5)_____, which are devices that use the
(6)_____ to convert light to electricity. As
atoms absorb energy, the electrons get
“excited” and release energy as (7)_____.
Whatever light that is not absorbed will
(8)_____ off the surface of the object and
bounce back toward the source.

Answers
Answer:
Light from the Sun reaches Earth very quickly. The (4) speed of light is 186,000 miles per second! We capture sunlight using (5) solar panels, which are devices that use the (6) photovoltaic effect to convert light to electricity. As atoms absorb energy, the electrons get “excited” and release energy as (7) photons. Whatever light that is not absorbed will (8) reflect off the surface of the object and bounce back toward the source.
There are about 4.7 billion tons of salt in the Great Salt Lake which results in extremely dense water. One weekend, a group of swimmers take a dive into this lake. True or False: As they begin to move around, they find it incredibly easy to stay afloat.
A. True
B. False
Answers
Answer:
A. True
Explanation:
Given that there is approx 4.7 billion salt tons in the Great Salt Lake due to which it extremely dense the water.
So if a group of swimmers dives in that so it would be easy to stay afloat as we know that the salt density is greater or more than as if we compared to the water that results into upward buoyant force is large
Therefore as per the situation, the given statement is true
The pressure at the bottom of a jug filled with water does NOT depend on the
__________.
A) depth of the liquid
B) acceleration due to gravity
C) density of water
D) surface area of the water
E) none of the above
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
because of the the side of the bottom
A 2kg basketball is sitting on the ground. A child exerts a force on the ball to lift it and attempt to shoot it into the basket. The ball leaves the child's hands at a velocity of 3m/s at a height of 2.5m. What is the change in total energy of the ball? What is the word done upon the ball?
Answers
Positive changes in the ball's total energy show that additional energy from outside the system was used to raise the ball and propel it into the basket.
If all forces acting on a moving ball are conserved, what happens to the ball's overall energy?If energy is conserved, the sum of an object's kinetic, gravitational potential, and heat energy—among others—might change forms as it moves about over time.
The ball's kinetic energy and potential energy combine to make its total energy:
E_total = U + K
Its initial potential energy is given by:
U_i = mgh = 2kg x 9.8m/s² x 0m = 0J
The amount of work done is equal to the ball's change in potential energy:
W = U_f - U_i
where U f is the ball's ultimate potential energy.
The ball's final potential energy is determined by:
U_f = mgh = 2kg x 9.8m/s² x 2.5m = 49J
As a result, the ball's work is as follows:
W = U_f - U_i = 49J - 0J = 49J
The ball's final kinetic energy is determined by:
K_f = 0.5mv^2
where v represents the ball's final speed.
Inputting the values provided yields:
K_f = 0.5 x 2kg x (3m/s)² = 9J
As a result, the ball's final total energy is as follows:
E_f = U_f + K_f = 49J + 9J = 58J
The change in total energy of the ball is:
ΔE = E_f - E_i = 58J - 0J = 58J
To know more about energy visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/30247873
#SPJ1
If you drop a 2.2 kg ball from the top of a 39 m high, how fast will it be going when it’s still 17 m above the ground? Round your answer to the nearest tenth and include the appropriate unit.
Answers
We are given that a ball is dropped from a height of 39 meters and we are asked to determine the velocity of the ball when it is 17 meters above the ground. To do that we will use the conservation of energy.
The energy when the ball is dropped is the gravitational potential energy and is given by the following formula:
\(E_1=mgh_0\)Where:
\(\begin{gathered} E_1=\text{ initial energy} \\ m=\text{ mass} \\ g=\text{ acceleration of gravity} \\ h_0=\text{ initial height} \end{gathered}\)Now, when the ball is 17 meters above the ground part of the gravitational potential energy has converted into kinetic energy. The kinetic energy is given by the following formula:
\(K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2\)Where:
\(v=\text{ velocity}\)Therefore, at the second point the ball has kinetic energy and gravitation al potential energy:
\(E_2=\frac{1}{2}mv^2+mgh_2\)Using conservation of energy we can set both energies equal:
\(mgh_0=\frac{1}{2}mv^2+mgh_2\)Now, we can solve for the velocity. To do that we will first cancel out the mass "m":
\(gh_0=\frac{1}{2}v^2+gh\)Now, we subtract "gh2" from both sides:
\(gh_0-gh_2=\frac{1}{2}v^2\)Now, we multiply both sides by 2:
\(2(gh_0-gh_2)=v^2\)Now, we can take "g" as a common factor:
\(2g(h_0-h_2)=v^2\)Now, we take the square root to both sides:
\(\sqrt{2g(h_0-h_2)}=v\)Now, we substitute the values:
\(\sqrt{2(9.8\frac{m}{s^2})(39m-17m)}=v\)Now, we solve the operations:
\(20.8\text{ m/s=}v\)Therefore, the velocity of the ball is 20.77 m/s.
Which of the following is true of a boat moving on water with
no net force acting on it?*
A. It is rising with increasing speed.
B. It is sinking with increasing speed.
C. It is traveling at a constant velocity.
D. It is accelerating forward.
Answers
x(t)=t^2-2t+1 when does it comes to rest?
Answers
Answer:
x(t) = t^2 - 2 t + 1 given
v = dx / dt = 2 t - 2 = 0
t = 1
It comes to rest after 1 second
in fig. 30-45, two straight conducting rails form a right angle. a conducting bar in contact with the rails starts at the vertex at time t 0 and moves with a constant velocity of 5.20 m/s along them. a magnetic field with b 0.350 t is directed out of the page. calculate (a) the flux through the triangle formed by the rails and bar at t 3.00 s and (b) the emf around the triangle at that time. (c) if the emf is at n, where a and n are constants, what is the value of n?
Answers
(a) The flux through the triangle formed by the rails and bar at t 3.00 s is calculated to be 85.2 Wb.
(b) The EMF around the triangle at that time is 56.8 V.
(c) If the EMF is at n, where a and n are constants, the value of n is 1.
(a) The height of the triangular area enclosed by the rails and bar is the same as the distance traveled in time t. So, we have d = v * t
where, v = 5.2 m/s
We also note that the base of the triangle is the distance between the intersection points of the bar with the rails which is 2 d. The area of the triangle is
A = 1/2 * b * h = 1/2 * 2 v t * v t = v² t²
As the field is said to be uniform B = 0.35 T
The magnitude of flux is given by,
Ф = B * A = 0.35 * v² t² = 0.35 * 5.2² * t² = 9.46 v² t²
At t = 3 s, we get Ф = 85.2 Wb
(b) The magnitude of EMF is
ε = dФ/dt = 9.46 dt²/dt = 18.9 t
At t = 3 s, ε = 18.9 t = 56.8 V
(c) Our solution part of (b) shows, n = 1
The question is incomplete. The attachment shows the figure.
To know more about magnetic field:
https://brainly.com/question/12984382
#SPJ4

In the 25 ftft Space Simulator facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a bank of overhead arc lamps can produce light of intensity 2500 W/m^2 at the floor of the facility. (This simulates the intensity of sunlight near the planet Venus.)
Required:
Find the average radiation pressure (in pascals and in atmospheres) on
a. A totally absorbing section of the floor.
b. A totally reflecting section of the floor.
c. Find the average momentum density (momentum per unit volume) in the light at the floor.
Answers
Answer:
a) 8.33 x \(10^{-6}\) Pa or 8.22 x \(10^{-11}\) atm
b) 1.66 x \(10^{-5}\) Pa or 1.63 x \(10^{-10}\) atm
c) 2.77 x \(10^{-14}\) kg/m^2-s
Explanation:
Intensity of light = 2500 W/m^2
area = 25 ft^2
a) average radiation pressure on a totally absorbing section of the floor\(Pav = \frac{I}{c}\)
where I is the intensity of the light
c is the speed of light = \(3*10^{8} m/s\)
\(Pav = \frac{2500}{3*10^{8} }\) = 8.33 x \(10^{-6}\) Pa
1 pa = \(9.87*10^{-6}\)
8.33 x \(10^{-6}\) Pa = 8.22 x \(10^{-11}\) atm
b) average radiation for a totally radiating section of the floor
\(Pav = \frac{2I}{c}\)
this means that the pressure for a totally radiating section is twice the average pressure of the totally absorbing section
therefore,
Pav = 2 x 8.33 x \(10^{-6}\) = 1.66 x \(10^{-5}\) Pa
or
Pav in atm = 2 x 8.22 x \(10^{-11}\) = 1.63 x \(10^{-10}\) atm
c) average momentum per unit volume is
\(m = \frac{I}{c^{2} }\)
\(m = \frac{2500}{(3*10^{8}) ^{2} }\) = 2.77 x \(10^{-14}\) kg/m^2-s
Which factors affect the gravitational force between two objects?
-
distance and velocity
O mass and distance
O mass and weight
acceleration and weight
TELE
Answers
Mass and distance
Explanation:
According to Newton’s law, “objects with greater mass have a stronger force of gravity between them.” And “objects that are closer together have a stronger force of gravity between them.” Both of them mean mass and distance. Therefore, the correct answer is mass and distance.
Answer:
mass and distance
Explanation:
mass, and distance. The force of gravity depends directly upon the masses of the two objects, and inversely on the square of the distance between them.
HONI A ball is rolling steady on the floor. (a) Draw and label all the forces acting on the ball. (b) Describe the relationships between all the forces acting on the ball
Answers
a) The image is attached to this answer
b) The kinetic friction force affects the forward force of the ball.
What is the relationship between the forces that act on a rolling ball?
The force that opposes a rolling ball's motion is called rolling friction. It slows the ball down by acting in the opposite direction to that of the ball's motion. The weight of the ball and the type of the surface are two variables that affect rolling friction.
The force that a surface uses to maintain the weight of an object that is resting on it is known as the normal force. When a ball is rolling, the normal force exerts itself perpendicular to the surface the ball is moving on. It maintains the ball's weight balance and offers the required reaction force for rolling motion.
Learn more about rolling ball:https://brainly.com/question/29409976
#SPJ1
A marble rolls with a speed of 15 m/s and has a momentum of 0.15 kg*m/s. What is its mass?
Answers
Answer:
m = 0.01 kg
Explanation:
Given that,
Momentum of the marble, p = 0.15 kg-m/s
Speed of the marble, v = 15 m/s
We need to find its mass. We know that,
Momentum, p = mv
Where
m is the mass
\(m=\dfrac{p}{v}\\\\m=\dfrac{0.15}{15}\\\\m=0.01\ kg\)
So, the mass of the marble is equal to 0.01 kg.
TRUE OR FALSE: Increasing the time of impact during a collision increases the force experienced by the object.
Answers
Answer: True
Explanation:
The precision value of measuring tape is
1)0.1cm
2)0.1mm
3)1cm
4)0.01cm
Answers
C.1cm
Explanation:
precision is how close two or more measurements are to each other
4?
Explanation:
sorry im not sure but
You can always take a metre ruler as a starting point. Your metre ruler has the same precision as your 15.0cm or 30.0cm ruler, so bring a ruler during exams as they'll come in handy ;)
The order goes like this:
rulers: 0.1cm or 1mm
measuring tape: 0.01cm or 0.1mm
vernier calipers: 0.001cm or 0.01mm
micrometer screw gauge: 0.0001cm or 0.001mm
((if i'm not wrong))
draw a molecule of carbon monoxide, CO, has ____ atoms.
Answers
If California experienced heavy rainfall, which system would be responsible for it and WHY?
Answers
Answer:
California has one of the most variable climates of any U.S state, and often experiences very wet years followed by extremely dry ones . The state's reservoirs have insufficient capacity to balance the water supply between wet and dry years.
PLEASE MARK ME AS BRAINLIEST
Archimedes and Heron are playing on a seesaw. Archimedes weighs 75 kg and Heron weighs 150 kg. If Heron is sitting 2 meters from the fulcrum, how many meters does Archimedes need to sit from the fulcrum?
Answers
Answer:
4metresExplanation:
Using the principle of moment to solve the problem. The principle states that the sum of clockwise moments is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moment.
Moment = force *perpendicular distance
Moment of Archimedes about the fulcrum = 75 * x ... 1
x is the distance of Archimedes from the fulcrum
Moment of Heron about the fulcrum = 150 * 2 = 300kgm... 2
Equation 1 and 2 according to principle of moment to get x we have;
75x = 300
x = 300/75
x = 4metres
Archimedes need to sit 4m from the fulcrum
A bowling ball moves with constant velocity from an initial posi-tion of 1.6 m to a final position of 7.8 m in 3.1 s.
(a) What is the position time equation for the bowling ball?
(b) At what time is the ball at the position 8.6 m?
Answers
Answer:
calculate 1.6*7.8*3.1
Explanation:
What is an induction?
Answers
Answer:
An induction is the process a new recruit goes through to be introduced to the company and their new role. ... Beyond the initial days, the induction programme continues for many months, so that the new employee can fully integrate into life in the company and settle into their role to become a valuable member of staff.
Explanation:
hope this help
pick me as the brainliest
A hollow glass sphere has a density of 1.3g/cm at 20 C. Glycerine has a density of 1.26 g/cm at 20 C. At what temperature would the sphere begin to float in glycerine
Answers
A hollow glass sphere has a density of 1.3g/cm at 20 C. Glycerine has a density of 1.26 g/cm at 20 C.
To determine the temperature at which the hollow glass sphere begins to float in glycerine, we need to calculate the density of glycerine at various temperatures and compare it to the density of the glass sphere.
The density of glycerine changes with temperature, so we need to use a density-temperature chart or equation to determine the density of glycerine at different temperatures.
Assuming the hollow glass sphere has a uniform wall thickness, we can calculate its volume by subtracting the volume of the hollow interior from the volume of the whole sphere
Volume of sphere = (4/3)π\(r^{3}\)
Volume of hollow interior = (4/3)π\((r-t)^{3}\)
Volume of glass wall = (4/3)π(\(r^{3}\) - \((r-t)^{3}\)), where t is the thickness of the glass wall.
From the density and volume of the glass sphere, we can determine its mass
Mass of glass sphere = Density of glass sphere x Volume of glass sphere
Next, we can use Archimedes' principle to determine the volume of glycerine displaced by the glass sphere when it is submerged in the glycerine
Volume of glycerine displaced = Mass of glass sphere / Density of glycerine at the given temperature
When the glass sphere floats, the volume of glycerine displaced will be equal to the volume of the glass sphere. Thus, we can set the two volumes equal to each other and solve for the temperature at which the density of glycerine matches the density of the glass sphere
Volume of glass sphere = Volume of glycerine displaced
(4/3)π\(r^{3}\) - (4/3)π\((r-t)^{3}\) = Mass of glass sphere / Density of glycerine at the given temperature
Hence, for the temperature requires knowing the radius and thickness of the glass sphere and the mass of the sphere.
To know more about Glycerine here
https://brainly.com/question/12925632
#SPJ1
If the total time is 120 seconds and the total distance is 320 meters. Calculate
the average speed (show work)
Answers
Answer:
S=D/T
320/120= 2.66 miles
Explanation:
Researchers studying the possible effects of “heading” a soccer ball--hitting it with the head--use a force plate to measure the interaction force between a ball and a hard surface. (Figure 1) shows smoothed data of the force when a 430 g
soccer ball is fired horizontally at the force plate with a speed of 15 m/s
With what speed does the ball rebound from the plate?

Answers
The speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
According to the graph, the greatest force exerted by the football on the force plate during impact is around 1900 N. The ball comes to a halt on the force plate before rebounding.
The kinetic energy of the ball before impact equals the kinetic energy of the ball after the rebound, according to the law of conservation of energy.
The speed of the ball rebounding can be calculated using the formula:
(1/2)mv²= (1/2)mv_0²
where m is the mass of the ball (0.43 kg), v is the speed of the ball rebounding, and v_0 is the initial speed of the ball (15 m/s).
Solving for v, we get:
v = sqrt(v_0² - (2F/m))
where F is the maximum force exerted on the force plate (1900 N).
Plugging in the values, we get:
v = sqrt(15² - (2*1900/0.43)) ≈ 13.2 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
learn more about speed here
https://brainly.com/question/13943409
#SPJ1
Drag the mass slider to give the skateboarder the largest mass possible. Drag and drop him on the three ramps, one at a time. Watch the kinetic energy bar as he travels down the ramps. Click the pause button right before he exits the ramp to freeze the action. Which ramp gives the skateboarder the greatest amount of kinetic energy? Which gives him the least? Now look at the speed dial. How does his speed relate to his kinetic energy?
Answers
1. Ramp 2. He gains the maximum kinetic energy from the steepest ramp.
2. Ramp 3 which is the flattest ramp should give him the least.
3. The greater his speed, the more kinetic energy he generates.
How is kinetic energy produced?
The simplest way to explain how kinetic energy is produced is; Motion produces kinetic energy. When there is some sort of movement, there is a likelihood of kinetic energy being produced.
Mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical energies can all produce kinetic energy.
For example, when Mechanical labor is done, a force acts on an item and causes it to move. This action then turns into kinetic energy.
Also, When an item is heated, the particles in it gain kinetic energy, raising its temperature.
Find more exercises on kinetic energy;
https://brainly.com/question/15764612
#SPJ1
Answer:
The steepest ramp gives the greatest amount of kinetic energy. The flattest ramp gives the least amount of kinetic energy. The middle ramp is in between. As the skateboarder’s speed increases, so does his kinetic energy.
Explanation:
pluto