you walk 12 meters north, then 10 meters west. What is your displacement
Answers
Answer:
Your displacement is 15.62m NW
Explanation:
We can use the Phytagorean theorem to determine the displacement:
a^2+b^2=c^2
12^2+10^2=c^2
144+100=c^2
244=c^2
15.62=c
So your displacement is 15.62m NW
Related Questions
What 4 pieces of information should be included any time you give a written
description of motion?
Answers
Answer:
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position over time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. ... One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries.
Explanation:
Two point charges, 9, = 1. 6 x 10-7 C and 92 = -6. 4 x 10-8 C, are held 37. 0 cm apart. (Assume q, is on the right. ) (a) What is the electric field (in N/C) at a point 5. 0 cm from the negative charge and along the line between the two charges? 2. 58825E5 X N/C magnitude direction to the right v (b) What is the force (in N) on an electron placed at that point? magnitude N direction to the left
Answers
(a) The electric field at a point 5.0 cm from the negative charge and along the line between the two charges is -2.58825 x 10⁵ N/C, directed towards the negative charge. (b) The force on an electron placed at that point is 2.58825 x 10⁻⁵ N, directed towards the positive charge.
The electric field at a point due to a point charge is given by the equation E = k * q / r², where E is the electric field, k is the electrostatic constant (k = 9 x 10⁹Nm² /C² ), q is the charge, and r is the distance between the charges.
(a) To find the electric field at a point 5.0 cm from the negative charge, we need to calculate the electric field due to both charges and then subtract the electric field due to the positive charge from the electric field due to the negative charge.
The electric field due to the negative charge (q2) is given by E2 = k * q2 / r², where q2 = -6.4 x 10⁻⁸ C and r = 5.0 cm = 0.05 m.
Plugging in the values, we get E2 = (9 x 10 Nm² /C² ) * (-6.4 x 10 C) / (0.05 m)² = -2.58825 x 10⁵ N/C.
The negative sign indicates that the electric field due to the negative charge is directed towards the negative charge.
(b) To find the force on an electron placed at that point, we need to calculate the force due to both charges and then subtract the force due to the positive charge from the force due to the negative charge.
The force between two charges is given by the equation F = k * |q1 * q2| / r², where F is the force, q1 and q2 are the charges, and r is the distance between the charges.
The force on the electron due to the negative charge (q2) is given by F2 = k * |q2 * e| / r², where q2 = -6.4 x 10⁻⁸ C, e is the charge of an electron (e = -1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ C), and r = 5.0 cm = 0.05 m.
Plugging in the values, we get F2 = (9 x 10⁹ Nm²/C²) * |-6.4 x 10⁻⁸ C * -1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ C| / (0.05 m)² = 2.58825 x 10⁻⁵ N.
The positive sign indicates that the force on the electron is directed away from the negative charge, which is towards the positive charge.
So, the answers to the given questions are:
(a) The electric field at a point 5.0 cm from the negative charge and along the line between the two charges is -2.58825 x 10⁵ N/C, directed towards the negative charge.
(b) The force on an electron placed at that point is 2.58825 x 10⁻⁵ N, directed towards the positive charge.
To know more about electron visit;
https://brainly.com/question/12001116
#SPJ11
An organ pipe is 151cm\; cm long. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. Part A: What are the fundamental and first three audible overtones if the pipe is closed at one end? What are the fundamental and first three audible overtones if the pipe is open at both ends? Express awnsers to 3 signiicant figures seperated by commas
Answers
For an organ pipe that is closed at one end and is 151 cm long:
Part A:
Fundamental frequency (first harmonic) = (speed of sound) / (2 x length of pipe)
= 343 / (2 x 1.51)
= 113.91 Hz
First overtone (second harmonic) = 3 x fundamental frequency
= 3 x 113.91
= 341.73 Hz
Second overtone (third harmonic) = 5 x fundamental frequency
= 5 x 113.91
= 569.55 Hz
Third overtone (fourth harmonic) = 7 x fundamental frequency
= 7 x 113.91
= 797.37 Hz
For an organ pipe that is open at both ends and is 151 cm long:
Fundamental frequency (first harmonic) = (speed of sound) / (2 x length of pipe)
= 343 / (2 x 1.51)
= 113.91 Hz
First overtone (second harmonic) = 2 x fundamental frequency
= 2 x 113.91
= 227.82 Hz
Second overtone (third harmonic) = 3 x fundamental frequency
= 3 x 113.91
= 341.73 Hz
Third overtone (fourth harmonic) = 4 x fundamental frequency
= 4 x 113.91
= 455.64 Hz
Learn more about organ pipe here:
https://brainly.com/question/24188759
#SPJ11
The fundamental frequency (first harmonic) of a closed-end pipe is given by:
f1 = v/4L
where v is the speed of sound in air and L is the length of the pipe.
For a closed-end pipe with L = 151 cm and v = 343 m/s, we have:
f1 = 343/(4 x 151/100) = 571 Hz
The frequency of the first overtone (second harmonic) is:
f2 = 2f1 = 2 x 571 = 1142 Hz
The frequency of the second overtone (third harmonic) is:
f3 = 3f1 = 3 x 571 = 1713 Hz
The frequency of the third overtone (fourth harmonic) is:
f4 = 4f1 = 4 x 571 = 2284 Hz
For an open-end pipe, the fundamental frequency is given by:
f1 = v/2L
where L is the length of the pipe.
For an open-end pipe with L = 151 cm and v = 343 m/s, we have:
f1 = 343/(2 x 151/100) = 1136 Hz
The frequency of the first overtone (second harmonic) is:
f2 = 2f1 = 2 x 1136 = 2272 Hz
The frequency of the second overtone (third harmonic) is:
f3 = 3f1 = 3 x 1136 = 3408 Hz
The frequency of the third overtone (fourth harmonic) is:
f4 = 4f1 = 4 x 1136 = 4544 Hz
Therefore, for a closed-end pipe with a length of 151 cm, the fundamental frequency is 571 Hz, and the first three overtones are 1142 Hz, 1713 Hz, and 2284 Hz.
For an open-end pipe with a length of 151 cm, the fundamental frequency is 1136 Hz, and the first three overtones are 2272 Hz, 3408 Hz, and 4544 Hz.
To know more about fundamental frequency :
https://brainly.com/question/29264927
#SPJ11
Which will not be affected by the induced e.m.f when a magnet is in motion relative to a coil? A. Motion of the magnet B. Resistance of the coil C. Number of turns of the coil D. The strength of the magnet pole
Answers
The strength of the magnet pole (option D) will not be affected by the induced electromotive force (e.m.f) when a magnet is in motion relative to a coil.
When a magnet is in motion relative to a coil, it induces an electromotive force (e.m.f) in the coil due to the changing magnetic field. This induced e.m.f. can cause various effects, but it does not directly affect the strength of the magnet pole (option D). Option A, the motion of the magnet, is directly related to the induction of the e.m.f. When the magnet moves, the magnetic field through the coil changes, inducing the e.m.f.
Option B, the resistance of the coil, affects the amount of current flowing through the coil when the e.m.f is induced. Higher resistance can limit the current flow. Option C, the number of turns of the coil, affects the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. More turns increase the induced voltage.
However, the strength of the magnet pole (option D) itself is independent of the induced e.m.f. It is determined by the properties of the magnet, such as its magnetization and magnetic material. The induced e.m.f does not alter the intrinsic strength of the magnet pole.
Learn more about electromotive force here:
https://brainly.com/question/13753346
#SPJ11
You ride your bicycle to the movie theater. you ride 30.km/hr north for 0.50 hours, and then 20.km/hr east for 0.25 hours
first change in position:
Equation:
Variables:
V=
D=
T=
Solution:
Second change in position:
Equation:
Variables:
V=
D=
T=
Solution:
Answers
The sum of the distances travelled in each direction equals the total distance travelled by bicycle:
According to the given data:Total distance = 15 km (north) + 5 km (east)
Total distance = 20 km
First change in position:
Equation: distance = speed x time (D = V x T)
Variables:
Speed (V) = 30 km/hr
Time (T) = 0.50 hours
Solution:
D = V x T
D = 30 km/hr x 0.50 hr
D = 15 km
The second change in position:
Equation: distance = speed x time (D = V x T)
Variables:
Speed (V) = 20 km/hr
Time (T) = 0.25 hours
Solution:
D = V x T
D = 20 km/hr x 0.25 hr
D = 5 km
Therefore, the total distance traveled by bicycle is the sum of the distances traveled in each direction:
Total distance = 15 km (north) + 5 km (east)
Total distance = 20 km
To know more about Variables visit:
brainly.com/question/25223322
#SPJ1
An inactive student wants to become more physically active but does not think he has the time. What is the most effective thing he can do to start making physical fitness a priority?
Answers
The most effective way for an inactive student to become more physically active is to make a schedule and stick to it. This can involve setting aside specific times for exercise each day.
How can one be physically active?Starting with small goals and gradually increasing the duration and intensity of their physical activity can also be helpful. Including physical activity into their daily routine like taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for a walk during lunch, can make it easier to fit exercise into their busy schedule.
Why is physical fitness important?Physical fitness is important for a number of reasons like improved Health, better mental health, increased energy, improved sleep and better brain functioning.
To know more about health, visit here:
https://brainly.com/question/13179079
#SPJ1
A cyclist is riding his bike up a mountain trail. When he starts up the trail, he is going 8 m/s. As the trail gets steeper, he slows to 3 m/s in 1 minute. What is the cyclist's acceleration?Felipe drives his car at a velocity of 28 m/s. He applies the brake, which slows the vehicle down at a rate of 6.4 m/s2 and causes it to slow to a stop. How long does it take for the car to stop? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Answers
Answer:
a) a = - 0.0833 m / s², b) t = 4.4 s
Explanation:
a) this is a kinematics exercise where the acceleration is along the inclined plane
v = v₀ - a t
a = v₀ - v / t
a = 3 - 8/60
a = - 0.0833 m / s²
b) in this case the final velocity is zero
v = v₀ - a t
0 = v₀ - at
t = v₀ / a
t = 28 / 6.4
t = 4.375 s
t = 4.4 s
Explain why the car in the photograph would get hot on a sunny day. How will the sunshield help to keep the car cool?

Answers
it will avoid the sun rays from penetrating into the glass to make it hot,and even fall on the seat and burn
Explanation:
Because of the type of metal it was made with
Answer:
The car gets hot in the photograph because of greenhouse effect. Most noticeably the fact that the sunlight enters the car through the windows to heat up the inside surfaces, which then gets trapped inside the car, causing a buildup of temperature.
Sunscreen can help keep the car cool by reflecting the sunlight, which in turn reduces the amount of heat that enters the car. This also decreases the inside surfaces to the exposure of UV lights.
leftover ice rich planetesimals are called
Answers
Help !!
If an object is placed 3 cm from the mirror, how far will the object appear “behind” the mirror?
Answers
Hope this helps!
Please give Brainliest!
This is because of the diagram below:

\(\qquad\qquad\huge\underline{{\sf Answer}}\)
As we know the property of a plane mirror, image formed by it is always virtual, of same Size as the object and at the same Distance as the object from the mirror. so we can say that the distance of image from the object = 3 cm from the mirror ( as per the property ) and at a distance of 6 cm from the object.
Which statement describes a credible source?
A-List comes from a website with advertisements and video
B- It features regular people opinions on the topic
C- It includes factual info supported by others sources
D- It is interesting to read and includes images with captions
Answers
Answer: C. It includes factual information supported by other sources
Explanation:
:) its really obvious tbh w you
gamertag: itzmamas1k
Answer:
Explanation:
its what he or she said i hope!
A car is traveling at 15. 5 m/s, and the driver sees a traffic light turn red. After 0. 321 s (the reaction time), the driver applies the brakes, and the car decelerates at 6. 2 m/s2. What is the stopping distance of the car, as measured from the point where the driver first sees the red light?
Answers
Stopping distance of the car, as measured from the point where the driver first sees the red light, is 43.95 meters We can use distance-time formula.
To calculate the stopping distance of the car, we need to determine the distance traveled during the driver's reaction time and the distance traveled while the car is decelerating.
During the driver's reaction time, the car will continue to move forward at its initial speed of 15.5 m/s. The distance traveled during this time is:
\(d_reaction = v_initial * t_reaction = 15.5 m/s * 0.321 s = 4.98 m\)
After the driver reacts, the car begins to decelerate at a rate of \(6.2 m/s^2\). Use equation:
d =\(v_initial * t + (1/2) * a * t^2\)
where d: distance traveled, v_initial: initial velocity, t: time, a: acceleration, and final velocity = 0 (since car stops).
We need to find the distance traveled during the deceleration period, so we can rearrange the equation to solve for d:
d = \((v_initial^2) / (2a)\)
Put values:
\(d_deceleration = (15.5 m/s)^2 / (2 * -6.2 m/s^2) = 38.97 m\)
Note that we used a negative value for acceleration, since the car is decelerating (slowing down) rather than accelerating (speeding up).
The total stopping distance is the sum of the distance traveled during the driver's reaction time and the distance traveled while decelerating:
\(d_total = d_reaction + d_deceleration = 4.98 m + 38.97 m = 43.95 m\)
Learn more about distance here:
https://brainly.com/question/29769926
#SPJ4
A circuit has a resistance of 8 Ohms. the voltage supplied to the circuit is 14 volts. what is the current flowing through it?
Answers
Answer:
e jiio7ruetw5258o0pomnmitwq2690okm ,,kkkiiht44456
The current across a certain resistor can be found using Ohm's Law, as before:
Vi = RiIi
where:
Vi is the voltage drop across the resistor
Ri is the resistance of the resistor
Ii is the current through the resistor
In this problem:
R2 = 8Ω is the resistor we are considering
V₂ = 110V is the voltage drop across that resistor (in a parallel circuit, the voltage drop is the same across each resistor)
Solving for I, we find the current through it:
I₂ = V₂/R₂ = 110/8 = 13.7A (see that "V₂/R₂" and "110/8" part as fraction)
IDK MORE POINTS BUT SAY SOMTHING FUNNY
Answers
Not the place for this but yesterday I ate a clock, it was very time consuming.
What is brown and sticky
A STICK GET YOUR MIND OUT OF THE GUTTER
PLEASE HELP
What is the force on a 1 kg ball that is falling freely due to the pull of gravity on Earth?
Answers
Answer:
9.8 N downward
Explanation:
The weight force is defined as w = mg, where m is the mass of the object and g = 9.8 m/s^2. Plugging in values shows that the force exerted on the ball is 9.8 N, downwards toward the ground.
crystalline regions help increase the of thermoplastics crystallinity in thermoplastics can be introduced by cooling or by induced crystallzation
Answers
Yes , Crystalline regions in thermoplastics help increase their strength, stiffness, and resistance to heat.
This is because the crystalline structure provides a more ordered arrangement of polymer chains, which increases the intermolecular forces and makes the material stronger.
Crystallinity in thermoplastics can be introduced by cooling the material from its molten state to its solid state, which allows the polymer chains to arrange themselves in a more ordered structure. This is known as "thermal crystallization."
Alternatively, crystallinity can be induced by stretching or orienting the material in a particular direction, which also causes the polymer chains to align themselves in a more ordered structure. This is known as "cold crystallization" or "orientation-induced crystallization."
To know more about thermoplastics refer here
https://brainly.com/question/13100040#
#SPJ11
What does this same experiment( the picture) tell you about light waves? Explain.

Answers
(refer to figure 24.) what is the approximate position of the aircraft if the vor receivers indicate the 245? radial of sulphur springs vor/dme (area 5) and the 140? radial of bonham vortac (area 3)?
Answers
The approximate position of the aircraft can be determined by the intersection of the 245° radial of the Sulphur Springs VOR/DME (Area 5) and the 140° radial of the Bonham VORTAC.
What is the VHF Omnidirectional Range?A VOR (VHF Omnidirectional Range) is a navigation aid that provides radial information from a ground station. In this case, the aircraft is receiving a signal indicating the 245° radial from the Sulphur Springs VOR/DME and the 140° radial from the Bonham VORTAC.
To determine the approximate position, the aircraft would need to plot these radials on a sectional chart or navigation display. The intersection of the two radials represents the approximate location of the aircraft. This is based on the assumption that the aircraft is on the specified radials and at the appropriate distance from each VOR station.
However, it's important to note that additional information, such as distance from the VOR stations or other navigational aids, would be needed for a more accurate position fix.
To know more about VHF Omnidirectional Range, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/27960001#
#SPJ4
Please help need answers and how to get them

Answers
The distance from the base of the cliff is 13.67 m.
The impact velocity of the block when it falls off the cliff is 15.3 m/s.
Initial velocity of the block, u = 15 m/s
Mass of the block, m = 5 kg
Coefficient of friction, μ = 0.3
Height of the cliff, h = 12 m
μmg = ma
a = μg
a = 0.3 x 9.8
a = 2.94 m/s²
At the initial surface,
Total energy of the block = 1/2mu² - mgh'
E = m(u²/2 - gh)
E = 5(15²/2 - 9.8 x 5)
E = 5 x 63.5
E = 317.5J
The impact velocity of the block when it falls off the cliff is given by,
1/2 mv² = mgh
v = √2gh
v = √(2 x 9.8 x 12)
v = √235.2
v = 15.3 m/s
The distance from the base of the cliff is given by,
R = v√(2h/g)
R = 15.3 x√(2 x 13/9.8)
R = 15.3 x 1.628
R = 13.67 m
To learn more about projectile, click:
https://brainly.com/question/28043302
#SPJ1
What is the wave speed if the wavelength is 5 meters and the frequency is 4 Hz?
Answers
The speed of wave is 20m/sec if the wavelength of wave is 5 meters and the frequency of the wave is 4Hz.
At the point when a wave goes through reflection, it simply stays in the medium and just switches its heading of movement. The smooth wave has voyaged twofold its distance. This reflection peculiarity of waves is regularly seen in sound waves.
At the point when you let out a noisy cry inside a ravine, you frequently hear the reverberation of the holler. The sound waves travel through the medium; for this situation, the air and bounce off the gulch wall and return to the beginning of the sound (you). The outcome is that you hear the reverberation of your holler.
We know that when a electromagnetic wave is travelling through speed v passing in a medium, it contains certain speed and wavelength which is given by the formula
c=ν × λ
where c is the speed of light in vacuum,
ν is the frequency of the wave and
λ is the wavelength of the wave.
Now, we have frequency(ν) = 4Hz, and wavelength(λ)=5meters.
So, using the above formula, we get
c=4 × 5
=>c=20m-Hz
or c=20m/sec as 1Hz=1 /sec
Hence, wave speed is 20m/sec.
To know more about wave speed, visit here:
https://brainly.com/question/10430072
#SPJ4
if an object falls with constant acceleration, the velocity of the object must
Answers
If an object falls with constant acceleration, the velocity of the object must increase uniformly over time. This means that the object's velocity will change by the same amount in equal time intervals.
Constant acceleration refers to a situation in physics where an object's velocity changes at a constant rate over time. It means that the object's acceleration remains the same throughout its motion. In other words, the object's speed increases or decreases by the same amount in equal intervals of time.
When an object experiences constant acceleration, its velocity changes linearly with time. Mathematically, this relationship is described by the equation:
v = u + at
Where:
v is the final velocity of the object,
u is the initial velocity of the object,
a is the constant acceleration, and
t is the time interval.
Additionally, the object's displacement (change in position) can be determined using the equation:
s = ut + (1/2)at^2
Where:
s is the displacement of the object
In a scenario where an object is falling due to gravity near the surface of the Earth, it experiences a constant acceleration known as the acceleration due to gravity, denoted by the symbol "g." The value of acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (9.8 m/s²) directed downward.
As the object falls, its velocity will increase at a constant rate. This implies that in equal time intervals, the change in velocity will be the same. For example, if the object's velocity increases by 10 meters per second (10 m/s) in the first second, it will increase by an additional 10 m/s in the second second, and so on.
In the case of an object falling with constant acceleration, the velocity of the object will progressively increase over time.
To know more about constant acceleration, visit
https://brainly.com/question/29135987
#SPJ11
If I hold an .63kg basketball 2 meters above the
ground, how much potential energy does it have?
If I drop the basketball from this height, how
much kinetic energy would it have right before it hits the floor?
Answers
Answer:
P.E.= 12.348 joules
K.E.=1.26 joules
Explanation:
For Q6. high school student holds a backpack one meter above the ground. Which of the following free-body diagrams best represents this situation?
Answers
The image that shows the free body diagram of the bag pack is option J.
What is the free body diagram?The term free body diagram has to do with the way the that the forces that act on an object are able to carry on. We know that an object is always acted upon by a system of forces. The forces that act on the object could be balanced or unbalanced. If the system of forces is balanced than the object would remain stationary. If the system of forces is not balanced then the object would move.
In this case, we have been told that high school student holds a backpack one meter above the ground. We know that we expect that the free body diagram would be able to show us the forces that act on the bag and this would include the weight of the bag which is the gravitational pull on it and the tension on the rope that holds the bag.
Learn more about free body diagram:https://brainly.com/question/10148657
#SPJ1

Express 48 m/s in terms of
1.km/h
2.m/min
3.km/s
4.km/minutes
Answers
48 m/s in terms of km/h is 720.8 km/h. In terms of m/min is 2880 m/min, in terms of km/s is 0.048 km/s and in terms of km/min is 2.88 km/min.
To solve this question, we need to understand some terms. The unit of velocity is measured in m/s. It can be expressed in different units of velocity.
1 km (kilometer) = 1000 meter
1 h (hour) = 3600 seconds
1 minutes = 60 seconds
To convert m/s into km/h,
48 m/s * 3600/1000 = 172.8 km/h
To convert m/s into m/min,
48 m/s * 60 = 2880 m/min
To convert m/s into km/s,
48 m/s ÷ 1000 = 0.048 km/s
To convert m/s into km/minutes,
48 m/s * 60 / 1000 = 2.88 km/min
Therefore, the 48 m/s expressed is 172.8 km/h, 2880 m/min, 0.048 km/s and 2.88 km/min.
To know more about velocity and conversions,
https://brainly.com/question/21552920
48 m/s is equivalent to 172.8 km/h, 2880 m/min, 0.048 km/s, and 2.88 km/minute.
To express 48 m/s in different units of velocity:
km/h (kilometers per hour):
To convert m/s to km/h, we can use the conversion factor of 3.6 since 1 m/s is equal to 3.6 km/h.
48 m/s * (3.6 km/h / 1 m/s) = 172.8 km/h
Therefore, 48 m/s is equivalent to 172.8 km/h.
m/min (meters per minute):
To convert m/s to m/min, we can use the conversion factor of 60 since there are 60 seconds in a minute.
48 m/s * (60 m/min / 1 s) = 2880 m/min
Therefore, 48 m/s is equivalent to 2880 m/min.
km/s (kilometers per second):
Since 1 kilometer is equal to 1000 meters, to convert m/s to km/s, we divide the value by 1000.
48 m/s / 1000 = 0.048 km/s
Therefore, 48 m/s is equivalent to 0.048 km/s.
km/minute (kilometers per minute):
To convert m/s to km/minute, we first need to convert m/s to km/s (as calculated in the previous step) and then multiply by 60 to convert seconds to minutes.
0.048 km/s * 60 = 2.88 km/minute
So, 48 m/s is equivalent to 2.88 km/minute.
Hence, 48 m/s is equivalent to approximately 172.8 km/h, 2880 m/min, 0.048 km/s, and 2.88 km/minute.
To learn more about escape velocity click:
brainly.com/question/29596174
#SPJ1
the law of conservation of energy
Answers
Answer:
what are the options
Explanation:
Answer:
The law of conservation of energy is a physical law that states energy cannot be created or destroyed but may be changed from one form to another Although, it may be transformed from one form to another. If you take all forms of energy into account, the total energy of an isolated system always remains constant.
Explanation:
Have amazing day!
Study the vector diagram.
Two vectors added using the tail to tip method. The first drawn north labeled Vector Y = 21 centimeters, the second drawn southeast labeled Vector Z = 75 centimeters, and the sum pointing east labeled Vector X = unknown.
What is the magnitude of vector X?
54 cm
72 cm
5184 cm
5625 cm
Answers
Answer:
B 72
Explanation:
The resultant of both the vectors will be 61.96 cm.
We have two vectors and their resultant.
We have to determine the magnitude of X.
What is a Vector quantity ?A quantity with both magnitude and direction is called vector quantity.
According to the question -
Vector Y = 21
Vector Z = 75
Refer the image attached.
Using the triangle law of addition -
\(\overrightarrow{X}=\overrightarrow{Y} + \overrightarrow{Z}\) = \(\sqrt{(21)^{2} +(75)^{2} +2\times 21\times 75\times cos(135)}\) = 61.96 cm
Hence, the resultant of both the vectors will be 61.96 cm.
To solve more questions on Vectors, visit the link below-
https://brainly.com/question/11134603
#SPJ2
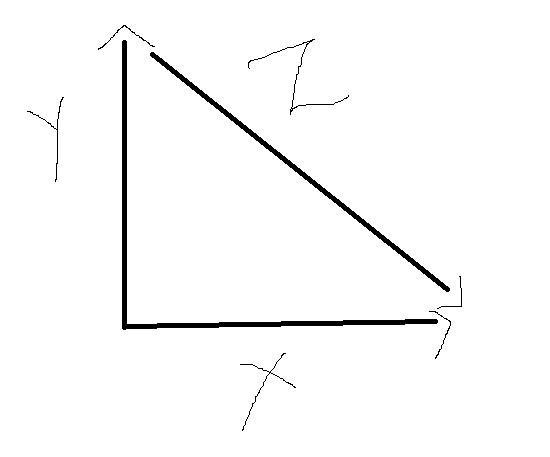
_________ describes an object's change in position. If the object returns to it's starting position, it is equal to zero. 2. _________ describes how far an objects has traveled. 3. _________________ is a measure of how fast something changes its position. In this case direction matters. It is also zero if an object has a displacement of zero. 4. ________________ is a measure of how quickly an object covers a distance per unit of time. If an object where to go around a circular track, this measurement would not be
Answers
Displacement describes an object's change in position. If the object returns to it's starting position, it is equal to zero.
Distance describes how far an objects has travelled.
Velocity is a measure of how fast something changes its position. In this case direction matters. It is also zero if an object has a displacement of zero.
Angular velocity is a measure of how quickly an object covers a distance per unit of time. If an object where to go around a circular track, this measurement would not be.
What is Velocity?When an item is moving, its velocity is the rate at which its direction is changing as seen from a certain point of view and as measured by a specific unit of time.
Displacement, Distance, Velocity, Angular velocity are correct answer.
To learn more about velocity refer to the link:
brainly.com/question/18084516
#SPJ1
How long will it take a projectile to hit the ground from a 400 m tall cliff when launched at 30 m/s horizontally?
19.55 sec
13.33 sec
9.03 sec
4.54 sec
Fast reply if possible
Answers
Explanation:
Baby Yoda weighs 53. 85N on Mercury; the gravitational force strength on Mercury is 3. 59 m/s2
[6 marks]
What is his mass on Mercury?
What is his weight on Earth?
If Baby Yoda is riding in an elevator that is accelerating down at a rate of 1. 25 m/s2, determine his apparent weight. (it may help if you draw a FBD)
Answers
Baby Yoda's mass on Mercury is 5.98 kg. His weight on Earth is 11.18 kg. His apparent weight in the elevator is 47.38 N.
To find Baby Yoda's mass on Mercury, we can use the formula:
weight = mass x gravitational force strengthRearranging the formula to solve for mass, we get:
mass = weight / gravitational force strengthPlugging in the given values, we get:
mass = 53.85N / 3.59 m/s² = 5.98 kgTo find Baby Yoda's weight on Earth, we can use the formula:
weight = mass x gravitational force strengthwhere the gravitational force strength on Earth is 9.81 m/s².
Plugging in the mass of 5.98 kg, we get:
weight = 5.98 kg x 9.81 m/s² = 11.18 kgTo find Baby Yoda's apparent weight in the elevator, we need to draw a free body diagram (FBD) and use Newton's second law:
apparent weight - weight = mass x accelerationThe weight is the gravitational force strength on Mercury, which we already know to be 53.85N. The apparent weight is the force that Baby Yoda feels in the elevator. The mass is still 5.98 kg, and the acceleration is -1.25 m/s² (negative because the elevator is accelerating downwards).
Plugging in the values, we get:
apparent weight - 53.85N = 5.98 kg x (-1.25 m/s²)Simplifying, we get:
apparent weight = 47.38 NTherefore, Baby Yoda's apparent weight in the elevator is 47.38 N.
To learn more about gravitational force, here
https://brainly.com/question/12528243
#SPJ4
The absence of any mechanical linkage between the throttle pedal and the throttle body requires the use of a _______ motor.
A. Throttle
B. AC
C. DC
D. Stepper
Answers
The absence of any mechanical linkage between the throttle pedal and the throttle body requires the use of a . Stepper motor. Option D.
In modern vehicles, the throttle system is commonly controlled electronically using a stepper motor. A stepper motor is a type of electric motor that moves in discrete steps or increments, as directed by an electronic control unit (ECU) based on inputs from sensors, including the throttle pedal position sensor.
With the use of a stepper motor, there is no direct mechanical connection between the throttle pedal and the throttle body. Instead, the ECU interprets the position of the throttle pedal and commands the stepper motor to move the throttle plate accordingly, regulating the airflow into the engine.
The stepper motor provides precise control over the throttle position, allowing for smooth and accurate adjustments based on driving conditions and engine demands. The ECU can precisely control the throttle opening angle and adjust it in real-time, optimizing fuel efficiency, emissions, and overall engine performance.
Stepper motors are particularly suitable for this application as they can hold their position without power, provide precise control over angular displacement, and offer good torque characteristics.
They are commonly used in drive-by-wire throttle systems, where electronic signals replace mechanical linkages, providing improved responsiveness and integration with other vehicle control systems.
In summary, the absence of a mechanical linkage between the throttle pedal and the throttle body necessitates the use of a stepper motor for electronic throttle control, allowing for accurate and efficient regulation of the engine's air intake. So Option D is correct .
For more question on linkage visit:
https://brainly.com/question/16767666
#SPJ8